
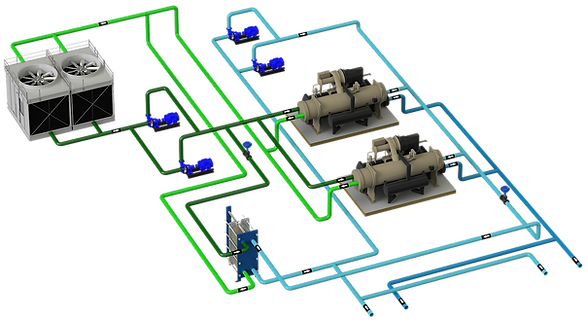
The heat produced in the refrigeration cycle must be dissipated to the outside. In water-cooled chillers, an external element such as a cooling tower, drycoolers or geothermal energy is required.

CONTENTS
-
Water-water chiller dissipation systems
-
Condenserless chiller dissipation systems
-
Heat pump dissipation systems
1 - GENERAL
This section excludes chillers and heat pumps that use outside air directly over a battery through which refrigerant circulates inside to dissipate excess energy from the cycle.
2 - DISSIPATION SYSTEMS FOR WATER-WATER CHILLERS
In water-cooled chillers, there are the following means of dissipation:
-
Cooling towers:
-
Based on evaporative air cooling
-
Design temperature, based on wet bulb temperature + approach
-
Good chiller performance by allowing moderate condensing temperatures
-
They can be open or closed, if the cooled water in the tower circulates throughout the circuit or is limited to the tower only.
-
Low electrical power in fans
-
Water consumption
-
Necessary maintenance for the prevention of legionella
-
Several possible configurations.
-
-
Drycoolers:
-
Based on the exchange of energy between air and water in a battery
-
Design temperature, based on outside temperature + approach
-
Optional adiabatic cooling of the exchange air, either by spraying water, humidification panels, etc.
-
Worse chiller performance due to working with higher condensing temperature
-
Greater electrical power installed in fans
-
They can be horizontal or V-shaped
-
Null or moderate water consumption in the case of adiabatic systems, depending on configuration
-
No maintenance necessary for the prevention of legionella
-
-
Geothermal:
-
Based on the use of natural resources such as land, seawater, well or lake
-
Stable temperature throughout the year and depends on the focus
-
Better chiller performance, the temperatures that allow condensation are usually lower than the previous ones
-
Higher initial investment cost for civil works or water pipes
-
-
Heat recovery systems:
-
Based on total or partial heat recovery from chillers, before dissipation to the outside. It is about taking advantage of the maximum heat potential when there is a demand for simultaneous cold and heat.
-
The working temperature will depend on the system to which heat is injected and therefore the performance of the chillers will depend on this value. They are usually higher than the temperatures achieved in towers or geothermal energy
3 - HEAT HEATING SYSTEMS FOR NON-CONDENSER CHILLERS
In water-cooled chillers, there are the following means of dissipation:
4 - DISSIPATION SYSTEMS FOR WATER-WATER HEAT PUMPS
In water-cooled chillers, there are the following means of dissipation:






